Tonya Lewis Lee's Hulu Documentary 'Aftershock' Investigates How To Reduce Black Maternal Mortality

Black women take center stage in April, celebrating International Black Women's History Month. In addition, April 11-17 sheds light on Black Maternal Health Week to raise awareness of the disparity of mortality rates among Black women compared to their non-Hispanic white counterparts. The discussions surrounding Black maternal mortality are becoming more mainstream with Baby Dove joining Sista Midwife Productions, "a birth advocacy, training, and consulting agency," to comprise a comprehensive list of the Black Doula Directory.
Tonya Lewis Lee has become a staunch advocate of ensuring that the American public is cognizant of alarming statistics that show "Black women are three times more likely to die from a pregnancy-related cause than White women" even though 80% of "pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are preventable," according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Bias, racial and gender inequities are prevalent in the American healthcare system, including other disparities such as "quality healthcare, underlying chronic conditions, and structural racism," all impair marginalized patients from having the same opportunities to receive care to uphold their "economic, physical, and emotional health," the CDC reports.
According to the organization's report, approximately 700 women die in the U.S. from pregnancy or various other pregnancy-related complications. Recently, in Detroit, Michigan, Alona White, a 25-year-old mother, died after giving birth to her second daughter; White succumbed to an emergency craniotomy that caused her brain to bleed. As a patient at Ascension St. John Moross, White underwent a C-section, a medical procedure that Lee’s documentary Aftershock also explores and shows the financial benefits hospitals and doctors reap from this particular surgery, even though it may not be conducive to the birthing process.
Lee, who co-directed and co-produced with Paula Eiselt, discusses through her documentary Aftershock about Black maternal health and places several human faces to those victimized by this growing health crisis. The Hulu doc, which is a part of the streaming service's Onyx Collective, initially premiered at the 2022 Sundance Film Festival in the U.S. Doc Competition and was awarded the Special Jury Award: Impact for Change. Aftershock follows Omari Maynard and Bruce McIntyre, who both lost their partners, Shamony Makeba Gibson and Amber Rose Isaac, during childbirth, and how the two men, along with other family members, are in the streets providing advocacy and activism to eradicate this epidemic.
Using her background as a former human rights attorney, a spokesperson for the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Office of Minority Health, and an author of the children's book Please, Baby, Please—which she co-wrote with her Academy awarding-winning husband, Spike Lee, she uses her platform to heighten the conversation of Black maternal health.
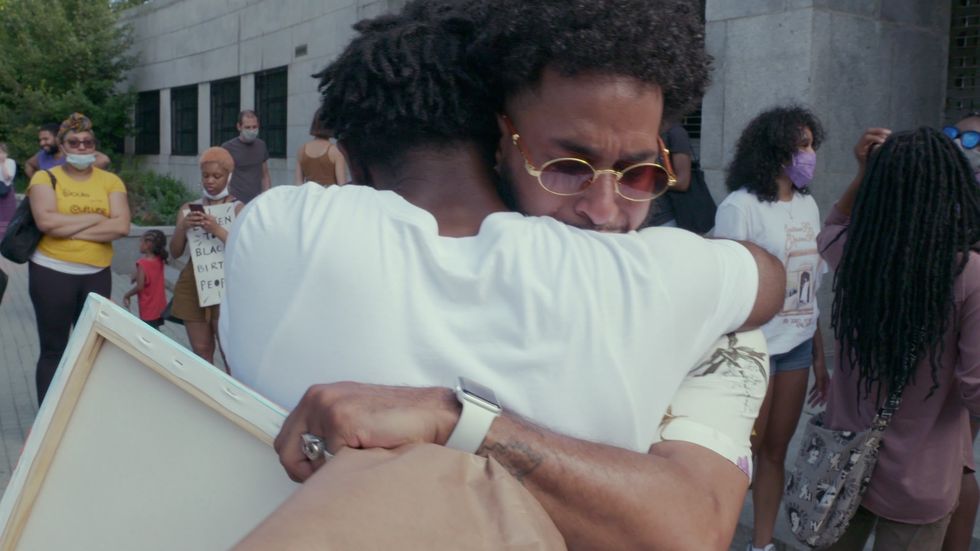

L-R Omari Maynard and Bruce McIntyre
Photo courtesy of Onyx Collective
xoNecole: Based on your research, what are the factors causing Black women's death in most hospitals? The documentary did expound on it, but if you can say it in your own words.
Tonya Lewis Lee: First, I want to say that most of these deaths happening with Black women from childbirth complications are preventable. When we were making the film, 65% of these deaths were preventable. Since then, a new statistic has come out that says 85% of these deaths are preventable. When you asked me what we discovered in our research about why this is happening? First and foremost, what keeps coming through is very clear that Black women are being dismissed and ignored when they express pain or discomfort or something is not right. A lot of these deaths are postpartum.
It's frustrating because it's not like women aren't seeking help, as you see in Aftershock. The two families that we cover, the two women who passed away, each of them were seeking help from their healthcare providers. Unfortunately, their calls for help were dismissed, minimized, and ultimately led to their death. I will say that what tends to happen is there is either too little intervention too late, or there tends to be too much intervention done too soon, which, unfortunately, often causes these deaths.
xoN: Is this something that residents are taught in medical school because, like the doc pointed out, the founder of gynecology J. Marion Sims, believed Black women don't feel pain? Is this ideology still continually introduced in medical schools?
TLL: My understanding, and I've heard, anecdotally, that it is still taught in med schools today that Black people do not suffer or have the same kind of pain that white patients do, which is insane to me that we're still having these conversations. I empathize with doctors because I think they are trained in such a way--it's a patriarchal, technocratic system. They go through rigorous training, which is great, but they're also kind of dehumanized doctors, when they're going through a process so that by the time they get to their patients, they often inadvertently treat their patients in the way they have to rush, let's get through to the problem. What's the problem? Let's solve it.
I'll go back to the question you asked before about what's causing these deaths also, is that [birthing] is not woman-centered, and what I mean by that is, when a woman is giving birth, as opposed to listening to her desires and how she wants to give birth and who she needs in the room, what is she doing and how is it working for her? Unfortunately, a lot of times, it's more on the doctor's schedule, what works for the doctor, and what's efficient for the doctor. Why do we lay on our backs and put our legs up? Well, because it's easier for the doctor to get in there than allowing a woman to move around during her labor to help the baby work its way down. So the baby gets in position, and she's able to do what she wants to do. I think that a lot of education works against the natural birthing process.
xoN: Regarding the medical schools, is there any way we can change how they're instructed? How can we upgrade their curriculum on how they handle Black maternity?
TLL: I agree with you, and I will say, at least some of the good news; I see that with Aftershock, we've been invited by medical schools to bring the film. We were at Harvard and Columbia [to show the film] to their residents and converse with me, my co-director, and the film's protagonist. To your point, they need to be educated; differently, they're beginning to understand that and are looking at it [but] it's going to take a little bit of time to turn the ship. But at least there's a conversation that is starting to happen, but I completely agree with you that med schools need to start thinking about how they teach maternal care.
And again, even the midwifery programs, too, because I am a big advocate for midwives. Yet, they're not enough midwives in general in the United States, and they're certainly not enough Black midwives. So, to that point, we also need to work on the pipeline of doctors, obstetricians, and gynecologists, because there's a shortage of doctors. There's a shortage of nurses, and certainly Black nurses and doctors. We want to think about who's going to med school and how we cultivate them so that we have a workforce that can care for all of us.
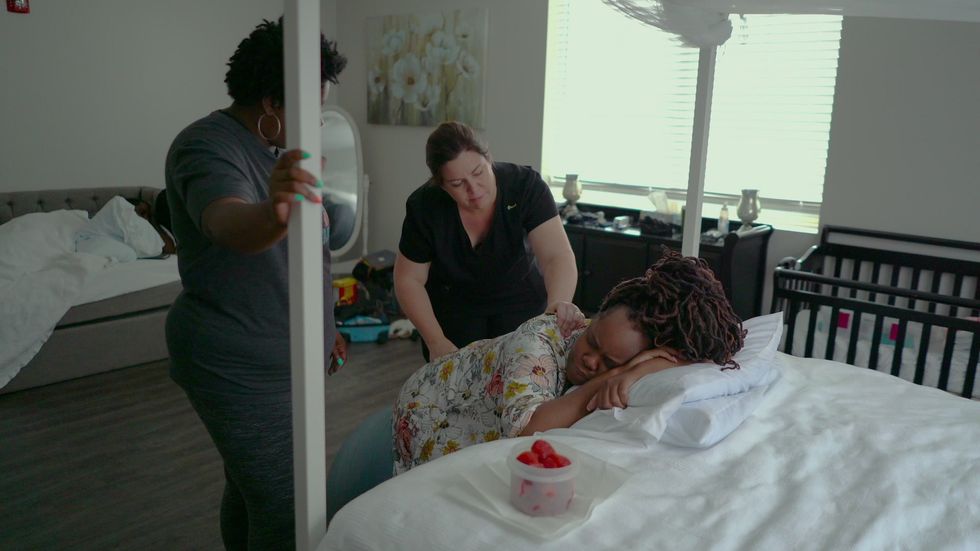

Photo courtesy of Onyx Collective
xoN: To add to that point, maybe there should be a movement to have Black owned hospitals. Many Jewish communities have their own doctors and ambulances. Is that also something we need to start putting on our agenda to start creating Black-owned hospitals in these cities with a high Black population?
TLL: I think we can [have] Black hospitals; we're talking about education in general. Our issue as a community is whether we need more resources or we need to focus the resources in that way. It's worth thinking about. Looking to our HBCUs, our Black students, bringing them through to get us to a place where we could create that kind of thing. I don't think it's a bad thing. A study showed that when Black doctors treat Black infants, they have better outcomes. So I think a movement towards ensuring that we have more Black doctors, more Black nurses, a robust Black health care system to begin with, or at least doctors. Having an awesome Black hospital that's important for us would be amazing because we do not have the resources to do that.
xoN: How can we change policy as it relates to the health of Black women when they're giving birth? What can we do?
TLL: Well, the good news is policies are moving through Congress right now, the Momnibus bills, its pieces of legislation, a group of bills. One in particular that is great that I believe recently passed is making sure that women have Medicaid coverage through their first year of birthing; I think it's important that we deal with women a year postpartum because, again, as I said earlier, most of these deaths do happen postpartum. Many women who don't have coverage get lost, and they don't see doctors thereafter or are not seen. We need to ensure policies that make sure that women have the support they need. For example, doulas get covered by insurance companies and Medicaid as well.
I think midwives are really important to this process; the United States is the only industrialized nation that does not have midwifery care at the center of women's health care. So we need to ensure that when women go to midwives, they can get reimbursed. So those are some policies that can have an impact. I will say voting matters because our politicians, locally at the federal level, but particularly locally, and our state and local governments are the ones that drive the policies and our communities around birthing. I think, as individuals, we need to be out there voting, ensuring women can get the support they need.
Also, to the voting piece because many hospitals in the Black communities have been divested from [offering] the services, if they do have maternal health care at all. They don't have a lot of services. So we want to make sure that our hospitals and our communities are well-resourced so that they can provide the care they need for people, especially when they're in distress.
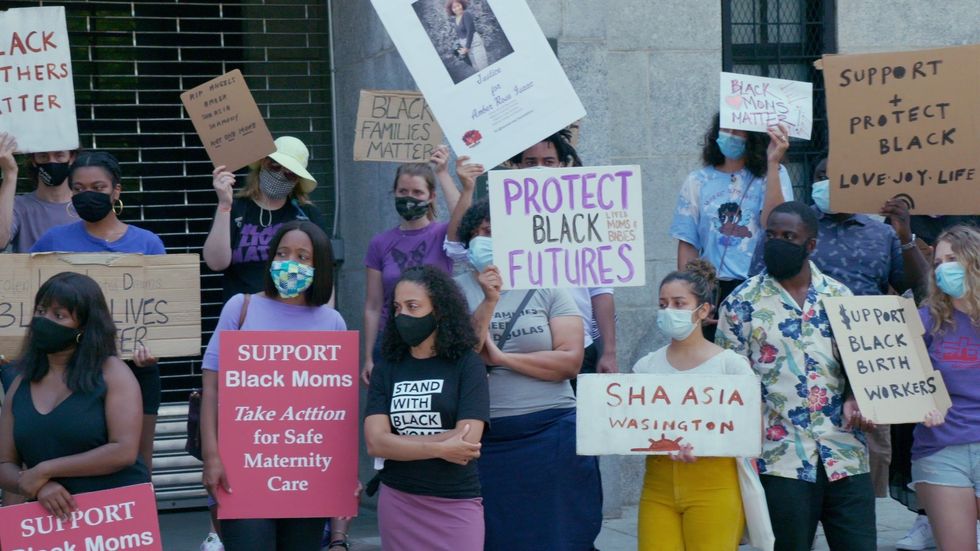

Photo courtesy of Onyx Collective
xoN: What was your experience when you gave birth to your children?
TLL: I appreciate that question. It's interesting. When I gave birth to my children, my daughter is now 27; my son is 25. I didn't know about midwives. So I had a wonderful doctor who was a friend of the family. But even then, I look back with a little frustration because my water broke, I went to the hospital, my family was there, and it was like, 'We can just move this thing along, let's get you on Pitocin get you going,' and I did that and stayed in the hospital overnight. Then the contractions were coming hard, as they do, especially when you're on Pitocin.
They suggested that I have an epidural, which I had. Then, my lips started to numb because they told me I was only supposed to be numb from the waist down. But I was beginning to feel numb over my entire body. I told my anesthesiologist to turn it down, my lips were numb, and she kept saying, 'Well, no, if I turn it down, I have to turn it off, and you're gonna feel pain.' I was like, I need to feel something because I'm now not feeling anything. I had to get nasty with her and didn't want to do it. Because you're laying there, you're vulnerable; I couldn't move. My mother and sister were there, and then they started noticing my oxygen levels were getting weird. I was like, 'You need to turn it off, and I had to get nasty for [the nurse to] finally turn down the anesthesia so that I can at least feel something. Thank God everything was fine, and my daughter was fine. Similarly with my son, a different doctor this time, by the way, both Black women, lovely people, but in a system, right?
With my son, the same thing happened; similarly, my water began to leak, and I was saved in a way by the nurse because at one point I was pushing, and the doctor was like, 'Okay, his umbilical cord is around his neck, his shoulders are stuck,' and she just stopped. The nurse said, 'This may hurt a little bit,' She put her hands on my stomach and pushed my son out. Again, I was fine, thank God, and the children are fine, but in retrospect, I wish I had allowed my body time to do what it wanted to do, and I think I would have been fine. I don't think I needed Pitocin. I don't think I needed the epidural if I had done it that way. But that's the way I did it back then.
But I joke with my daughter that by the time she's ready, I'm ready, and we're going to get it right this time because I don't think that surviving birth is what it should be. I think we should thrive in our births and be able to have beautiful birthing experiences that are not with trauma. And I'm not saying they don't have pain, but I believe that the pain that one goes through is what we're supposed to go through. I don't think women should suffer. But as Helena Grant, the midwife in our film, says that when a woman is birthing a baby, she's not just birthing a baby, she's birthing a mother, and it's a rite of passage that we have to go through to get on that other side. So we are prepared to take care of this young life we've just brought here.
xoN: How can women protect themselves when pregnant or about to give birth in this environment?
TLL: First of all, shop around for your healthcare provider. If you go to a health care provider and you don't connect with them, then keep looking for that health care provider that is right for you. First and foremost, ask as many questions as you can ask. Remember that you're in the power seat, you should be empowered; you're about to go through something amazing. Make sure you get the support you need. No [woman] can be doing everything in the moment of labor and birthing.
So make sure you have the right energy and people around you who can advocate for you and support you the way you need during your birthing process. I was with these people through the process of this documentary. I was able to be up close and personal with people grieving from a loss but activated by the loss. I was able to be up close and personal with people going through the birthing process themselves, trying to figure it out for themselves as well. So it's been quite a journey.
Aftershock is now streaming on Hulu.
Let’s make things inbox official! Sign up for the xoNecole newsletter for daily love, wellness, career, and exclusive content delivered straight to your inbox.
Feature image by Keith Williams
Your December 2025 Monthly Horoscopes Are All About Surrender & Alignment
December is about letting go. We end the year with the need for more peace, reflection, and rejuvenation, and that is exactly what December is providing for us. The Sun is in Sagittarius, and anything is possible. This is the month to believe in that and to know that the universe is supporting you. With a Supermoon in Gemini as we begin the month as well, we have an opportunity to gain the closure we have been looking for this year and to wrap up old projects, ideas, and communication breakthroughs.
This is the month to make your peace the priority and let go of trying to control the way the tides are turning. Trust in your new beginning, and give yourself time to prepare for it this month.
A big part of the clarity that is coming through this month is due to Neptune going direct in Pisces on December 10, after being retrograde here since July. With Neptune now direct, we are able to see our inspiration and creativity a little more clearly, providing the perfect energy for dreams and manifestation to be built upon. The smoke is clearing, and it’s up to you to decide what you want to do with this newfound clarity that this transit is bringing. Mercury also moves back into Sagittarius on December 11, which is great for communication and clarity, and the adventures you were trying to see through at the beginning of November come around for you again with greater purpose and support.
On December 15, Mars enters Capricorn until the end of January 2026, and this is the extra push we need to make important changes and to be on the path towards greater abundance, stability, and prosperity. Mars in Capricorn takes care of business, and we have extra energy at our disposal during this time to do so. This transit is an ideal time to focus on your career or financial goals for next year and to start putting some of these plans into motion now. A few days later, we have the New Moon of the month, which will be in Sagittarius on December 19, and this is the perfect New Moon to manifest.
The energy is high, magic is in the air, and it’s all about moving forward with the new beginnings that are inspiring you and bringing you joy to think about right now.
Capricorn Season officially begins on December 21, and this earth sign energy is how we heal, gain closure, and build new foundations in our world. With Venus also moving into a Capricorn a few days later, there is something about peace, prosperity, and security that we are gaining in life and in love as we close out the year, and this is what we need right now. This month is about reflecting on what was, letting go of old hurt, and renewing. December is an ending and a new beginning in one, and there is magic in this space to be created.
Read for your sun and rising sign below to see what December 2025 has in store for you.
 AriesKyra Jay for xoNecole
AriesKyra Jay for xoNecoleARIES
December is a full-circle moment for you, Aries. You are seeing the gifts in your world and have a lot of gratitude for the way things have come about for you as of late. There are culminations in your world that are providing you with more abundance, stability, and community, and you are exactly where you are meant to be this month. With the Sun in a fellow fire sign and in your 9th house of travel for most of the month, December is a good time to get out of your comfort zone, explore the world around you, and get your body moving.
Mars, your ruling planet, also makes a change and moves into Capricorn on December 15, which will fuel your inspiration and power in your career space. You are making a lot of professional progress as we close out the year; however, make sure to be more mindful of your competitive drive right now. The New Moon on December 19 is the perfect opportunity for you to create some new plans and goals when it comes to traveling, education, and where you want to gain some new inspiration in your world. Overall, this is a month of things coming together for you serendipitously.
 TaurusKyra Jay for xoNecole
TaurusKyra Jay for xoNecoleTAURUS
December is about trusting your intuition, Taurus. You have a lot on your mind this month, and it’s best to delegate, communicate, and allow yourself some relief by opening up to someone and not feeling like you have to hold everything in. As we begin the month, we have a Supermoon in Gemini happening in your house of income, and the plans and projects you have been building here come to fruition for you now. This is the time to gain clarity on your financial world and to take a look at what spending habits you want to let go of here as well.
With Venus in your 8th house of shared resources for most of the month, you are doing a cleanse on your commitments, partnerships, and business ventures. You are taking a look at what you want to dedicate yourself to in the future, and what commitments you may need to let go of now in order to be in the space you truly want to be, both financially and within some of your relationship dynamics. Before we end the month, we have a New Moon in this same area of your chart, and it’s time to look at the opportunities that are presenting themselves and to trust your internal guidance system to lead you forward.
 GeminiKyra Jay for xoNecole
GeminiKyra Jay for xoNecoleGEMINI
You are moving forward fearlessly this month, Gemini. December is your month of love, passion, and dignity, and you are owning the light that you shine. We begin the month with the last Supermoon of the year, happening in your sign, and you are stepping up to the plate. You are showing up, owning how much you have grown this year, and allowing yourself to heal while also acknowledging that you have done your best and you deserve to have fun in the midst of the changes you are creating.
Mercury, your ruling planet, is officially out of retrograde, and you can use this energy to the fullest potential now. With Mercury in your 7th house of love, it’s time to speak from the heart and to talk about the things that matter and that are inspiring you right now to your loved ones. You never know what kind of epiphanies you may have when you open up the conversation to others. Before the month ends, you have a New Moon in this same love area of your chart, and this New Moon is all about manifesting romance, commitment, and abundance in your world.
 CancerKyra Jay for xoNecole
CancerKyra Jay for xoNecoleCANCER
December is an opening for more love, more joy, and more freedom in your life, Cancer. You have come to a place where you hold so much gratitude in your heart for where you are today and where your heart is shining, and things come together for you with more ease right now. With the Sun in your 6th house of health, work, and daily routines for most of the month, you are getting your ducks in a row while also putting more energy and effort into taking care of yourself, your priorities, and your well-being. This month surprises you in many ways, and it’s because you are showing up.
Mars and Venus both move into your house of love, relationships, marriage, and abundance this month, and you are making strides in your love life. You have both of these opposing forces on your side and are being recognized for the love you are while also receiving the love you want. This month, overall, is about focusing more on the positives in your world and letting your heart have its joy. Before December comes to an end, there is a New Moon in Sagittarius, and this is the perfect opportunity to create the plans you want to see through next year, especially when it comes to your work life, colleagues, business ventures, and health.
 LeoKyra Jay for xoNecole
LeoKyra Jay for xoNecoleLEO
The scales of karma are balancing, and they are balancing in your favor this month, Leo. December is your month of truth, and of seeing it clearly in your world. The Sun is in your house of romance, pleasure, and happiness for most of the month, and it’s time to relax, be in the present moment, and allow what is meant to be, to be. With a Supermoon in your 11th house of manifestation as December begins, this is a powerful month for seeing your dreams come to fruition, and for feeling like the intentions you have set this year are finally here for you now.
Mars also moves into your 6th house mid-month, and this is the perfect energy to have to move into the new year. You have extra energy at your disposal right now and are feeling fearless with what is possible for you and your daily routine. Before the month ends, we also have a New Moon in a fellow fire sign, Sagittarius, and this is a breakthrough moment for you and your heart. December, overall, wants to show you how loved and supported you are and will be doing so in magical, unexpected, and concrete ways.
 VirgoKyra Jay for xoNecole
VirgoKyra Jay for xoNecoleVIRGO
December is a month of victory, Virgo. You are showing up and experiencing some new successes in your world that move you forward on your path in life. With a Supermoon in your 10th house of career as we begin the month, the effort and intentions you have made this year come into full bloom, and you are being recognized for who you are and the good work you have done. This month is all about showing up and allowing yourself to be seen and loved, knowing that you deserve the support and opportunities you are receiving.
Mars moves into Capricorn on December 15, which brings the passion and excitement into your love life, hobbies, and little pleasures in life that light you up. You want to have fun this month and are going to be walking into the new year with this fearless, happy, and spontaneous energy within you. Before the month ends, Venus also enters Capricorn, and in this same area of your chart, you have a lot to look forward to and believe in right now. Overall, December wants you to be happy and will be doing everything possible to make that happen for you. This is your month to shine, Virgo.
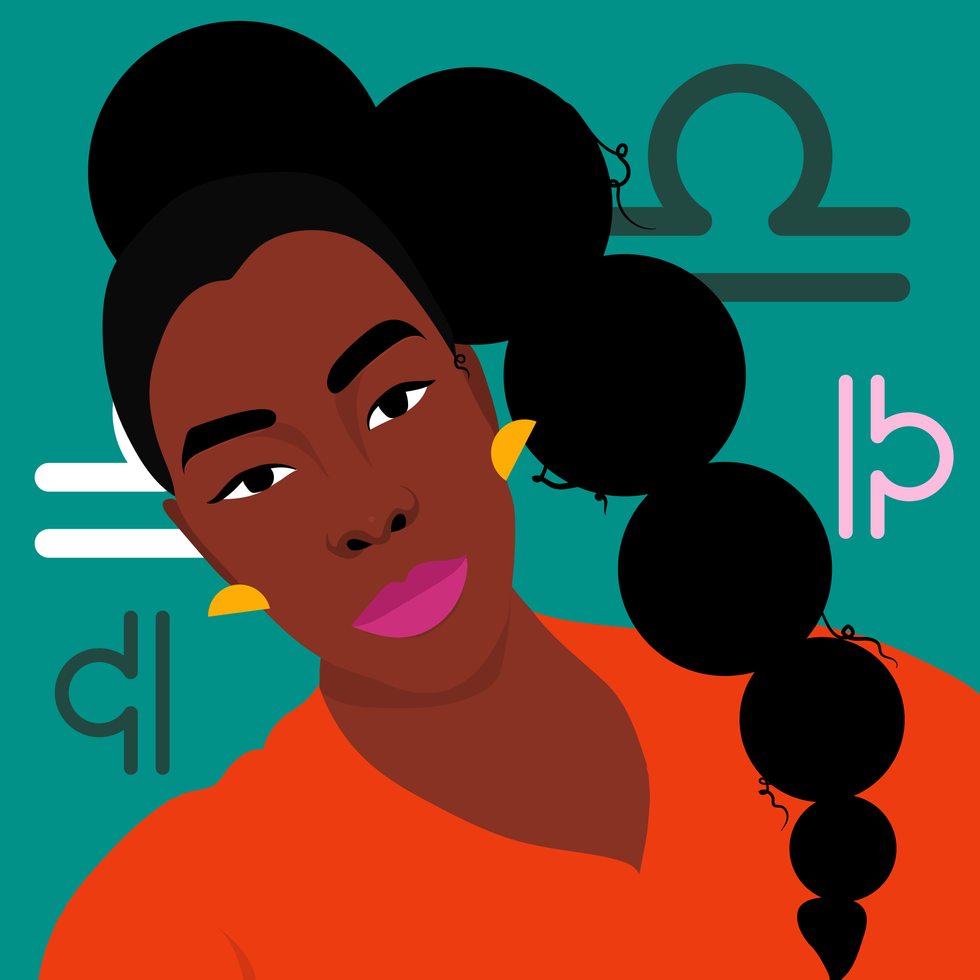 LibraKyra Jay for xoNecole
LibraKyra Jay for xoNecoleLIBRA
December is a month of opportunity for you, Libra. New doors open, and you are financially making breakthroughs this month because of it. December begins with a Supermoon in your 9th house, and you are getting a clearer view of where you have been making strides in your life and how it has all brought you here to this present moment of freedom. This month is showing you what happens when you are fearless with your purpose and when you believe in yourself and what you are worthy of.
Moving further into December, Mars moves into your 4th house of home and family mid-month, and you are closing out the year in your safe spaces. You are spending more time with your loved ones and taking the time to quiet your mind and listen to what your heart has been telling you. Before the month ends, we have a New Moon in Sagittarius, happening in an area of your life that deals with communication. This is a great time for getting the answers you have been looking for and for feeling more clear-headed and confident about the decisions you are making as you move into the new year.
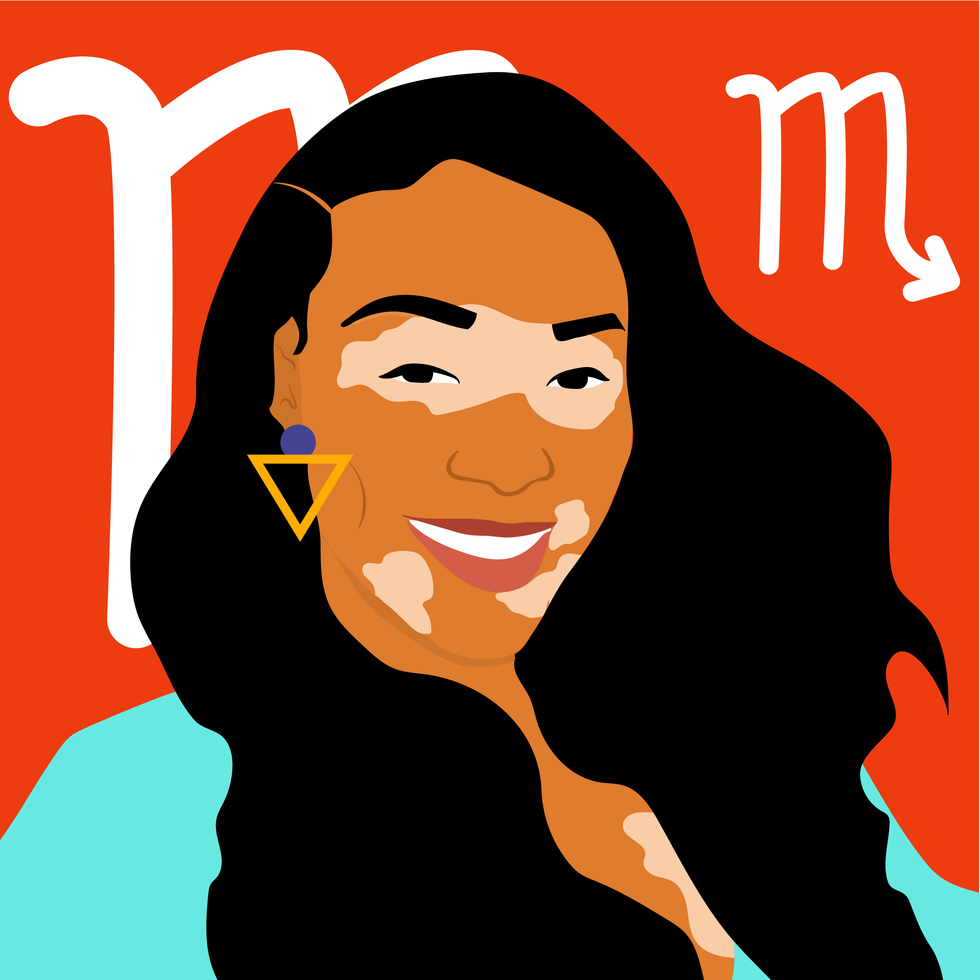 ScorpioKyra Jay for xoNecole
ScorpioKyra Jay for xoNecoleSCORPIO
Patience is a virtue this month, Scorpio. December is all about remaining patient and vigilant with what you are creating in your world, and knowing that the universe has your back. It’s time to be reminded of the power of hope, and this month is an opening to greater clarity in your life. There is a lot of energy in your financial zones right now, and this is providing you with new opportunities and new insight; however, the speed at which things come about for you may feel daunting. Keep your head up and eyes focused on what you want and know that you are more than worthy of receiving it.
With Mercury in your 2nd house of income this month, December is a good time to plant new seeds and to think about where you want to be financially a month from now or even a year. This month is asking you to think bigger and to think more long-term so that you can set the appropriate plans into motion now. We also have a New Moon in your house of income before the month ends, and this is when you will see more of your dreams come to fruition in this area of your life, and have more opportunities to build. Overall, December will be teaching you a lot, Scorpio.
 SagittariusKyra Jay for xoNecole
SagittariusKyra Jay for xoNecoleSAGITTARIUS
Sagittarius Season is here, and there is a lot in store for you this month, Sag. December is all about what you are dedicating yourself to. It’s about setting your intentions and putting the work in to back up your dreams, and about getting things in order so that when the new beginnings come, you are ready for them. The Sun and Venus are in your sign for most of this month, and there are a lot of eyes on you right now. You have the potential to create a new beginning for yourself, and it’s time to invest in yourself, your love life, and your dreams.
Mercury moves into Sagittarius on December 11, and this is giving you another opportunity to see through some of the plans that you had initiated in November. Mercury was retrograde in your sign last month, and there may have been some disruptions to your vision and plans for the future, and now this energy is turning around for you. Before the month ends, we also have a New Moon in Sagittarius, and you are walking through new doors fearlessly. You are catching others by surprise by your growth this month, and you are thinking a lot about your purpose, future, and plans for the new year.
 CapricornKyra Jay for xoNecole
CapricornKyra Jay for xoNecoleCAPRICORN
December is all about the vision, Capricorn. You are moving through a lot of changes and transformations this month, yet they are giving you a chance at a new beginning in the process. You are focused more on the future and what goals you want to manifest for yourself right now, and are ready to let go of what hasn’t been working for you. With the Sun in your 12th house of closure for most of December, this is your time for healing, but remember, healing doesn’t have to be isolating or boring; you can thrive while you renew, and you are this month.
Mid-month, the excitement picks up for you, and you are feeling more energized than you have in a while. Mars moves into Capricorn until the end of January 2026, and you are being proactive with your goals, intentions, and passions. You are a force to be reckoned with this month, and you are making things happen for yourself with confidence. Capricorn Season officially begins on December 21 this year, and this is definitely speeding up your healing process. You are breaking free from what was, and with Venus also moving into Capricorn before the month ends, you are leaving this year in high spirits and with love opening a new door for you.
 AquariusKyra Jay for xoNecole
AquariusKyra Jay for xoNecoleAQUARIUS
December is all about community, creativity, and manifestation, Aquarius. This is the month to work together with others to help bring your dreams to life. You are in a space of inspiration, empowerment, and beauty, and are creating more of this energy around you and in your world. Look out for what support comes your way this month and know that you don’t have to do everything alone to succeed. With the Sun in your 11th house of manifestation and friendship, your intentions are coming to fruition, and it’s time to celebrate with the people you love and to own how far you have come this year.
On December 19, we have a New Moon in Sagittarius, lighting up your life in all of the best ways possible. This is your New Moon of freedom, victory, and magic, and you are seeing new beginnings appear that you were once just hoping for. Before the month comes to an end, Venus moves into your 12th house of closure, and after an active and successful month, you are ready to relax, heal, and give your heart some of the attention it has been asking for. You are moving into the new year with the need to release and renew what hasn’t been working in your relationships, and you are finally ready to.
 PiscesKyra Jay for xoNecole
PiscesKyra Jay for xoNecolePISCES
December is a big month for you, Pisces. You are making some huge accomplishments this month, and are feeling like everything you have been through this year has been worth it for these moments that are coming to fruition for you now. The Sun is in your 10th house of career and reputation for most of the month, and this is where a lot of your focus is right now. You are claiming your successes and putting yourself out there in ways that not only serve you, but that inspire others as well.
Neptune officially goes direct on December 10, after being retrograde in your sign since July, and you are finally seeing things a little more clearly. You are feeling renewed inspiration and passion in your life, and your intuition is your strongest asset right now. Before December comes to an end, we also have a New Moon in your 10th house of career, and what happens now not only changes things for you in the present, but it also opens new doors and what is possible for you in the new year as well. Overall, you are on top of your game this month and are owning the joy and empowerment you feel.
Featured image by Kyra Jay for xoNecole
You're Over Him. Should You Wait Until After The Holidays To Say It?
When a client told me that she was seriously considering ending her relationship of 10 months before Christmas, I wasn’t surprised. That’s not a sneak diss on what she has going on with her man or anything; it’s just that I know that the holiday season (the month of December, more specifically) is a very popular time for folks to call things off. Between the pressure of bringing people around family and the urge to start off the new year with a clean slate — yeah, it makes sense.
At the same time, though, I do think that there is something to be said for ending things well — and when it comes to a break-up? During this time of the year? Before you make that official move, I just want to make sure that you’ve thought a few things through.
Things like what exactly? So glad that you asked.
How Serious Is the Relationship?
 Giphy
GiphyOkay, so if you’ve never heard of the “10-date rule” before, it’s basically the belief that after 10 consecutive dates with someone, it’s time to come to the conclusion that you are officially in a relationship with them. Personally, I have lived, observed and counseled enough people to say that when it comes to knowing where you stand with another person, you shouldn’t assume one damn thing — you should 1000 percent communicate your thoughts and listen to theirs in return.
That said, it is a bit different (wouldn’t you say?) if you’ve been out on a couple of dates with someone vs. if you’ve been with them for almost a year. So yeah, the first thing to ponder is how serious the dynamic is. Because honestly, if things are new and fairly casual, I don’t see how ending things, whether it’s the holiday season or not, is going to matter much — one way or another.
Remember, the holidays tend to be a very emotional time; however, if there isn’t a huge emotional investment going on, I don’t think anyone in a casual situation is going to look back and think that you are a villain (or Grinch), just because you’d prefer not to go on a third date with them. Good lord.
Next point.
Do You Want to Slow Down or End Things Entirely?
 Giphy
GiphyAre you totally over him or is it more like there are some things about the situation that you want to step back and ponder before making any major decisions about the future? If the answer is “B,” I recommend talking it over ASAP; especially if the two of you have been seeing each other for a while at this point. I say this because, whether you all are at the “meet the family” (or have already met the family) stage or not, when people are in a relationship, they tend to factor one another into their holiday plans — and it’s hella inconsiderate to not take this into account when it comes to the guy who you are seeing.
That said, I will say this: It’s mighty interesting that you are choosing this time of the year for this type of relational self-reflection — so, while you’re on this break, think about what it symbolizes.
For instance, are you slowing things down right now because you’re not sure if you want to go into a new year with him or are you doing it because spending the holidays together tends to represent that a relationship is far deeper than you want yours to be right now? Because really, you could’ve gone with the summertime (for example) not the holiday season to make this type of move…so, if your “pump the brakes” time is now, chances are, there is some subconscious subtext going on that you really should get to the root of.
Actual Holidays Are a DEFINITE No-No
 Giphy
GiphyYou would think that this wouldn’t need to be said yet since I once experienced a guy who decided to be a complete a*shole on my birthday some years back — yeah, let’s address it. Isn’t it interesting that one study revealed that during the first week of December, searches for how to break-up with someone go up by a whopping 60 percent? Then, if you add to that the fact that the holidays can sometimes be pretty stressful — well, while most folks with a heart and a conscience wouldn’t dream of breaking up with someone on an actual holiday, sometimes the pressure of everything can create the perfect storm for it to happen anyway.
That said, a super-duper throwback song by Neil Sedaka entitled, “Breaking Up Is Hard to Do” — and it absolutely is. Know what makes it worse: It happening on a holiday, so that every time the day rolls around, it’s bittersweet because you remember that someone broke up with you then.
Listen, just because you may not love or even like someone (in that way) anymore, that doesn’t mean that you shouldn’t treat them with some common decency and respect. Besides, don’t you also want your own Thanksgiving, Christmas Eve, Christmas Day, New Year’s Eve and New Year’s Day to be as unscathed and drama-less as possible?
Whatever you’re gonna do, you’re grown, chile. If you want my advice, though — put good energy into your future holiday seasons and avoid breaking up (or even having deep decisions) on actual holidays.
Definitely Keep the Golden Rule in Mind
 Giphy
GiphyProbably, until the end of time, there are going to be debates about whether karma is real (in the sense of it being scientifically proven). While quite a bit of data says that it isn’t and that it tends to be adapted and promoted by certain faiths more than anything — if you do believe that you reap what you sow (Galatians 6:7-8), at the end of the day, that is pretty much what karma is all about and, as I oftentimes say, karma (or sowing and reaping) don’t have expiration dates. In other words, what you have said and done can manifest in ways and at times that you never saw coming. A cautionary tale, indeed.
So yeah — even if you’ve been with ole’ boy for a while now, you’ve tried to make it work and you just don’t see a future for the two of you anymore, however you decide to end it, definitely keep the golden rule of doing unto others as you would want them to do unto you in mind.
Be as kind as you are honest. Be as empathetic (putting yourself in his shoes) as much as you possibly can. Avoid gaslighting him about how he feels about your decision. Be clear about how you’d like things to be moving forward (for instance, if you actually DON’T want to be friends afterwards, there’s no need to say it). And try not to do anything that will make him feel used — like waiting until after receiving a Christmas gift to end it (you’d be amazed by how many people do exactly that. SMDH).
The thing about break-ups is, live long enough, and you’re probably going to be on the giving and receiving end of one. So, even if you’re not really emotionally invested in your relationship anymore, be kind to your future self and be as respectful as possible throughout your…relational transition. Because even if you don’t feel like he deserves it, your feelings up the road, with someone else who may do the same thing to you…absolutely do.
Timing Is Everything
 Giphy
GiphyA bishop by the name of Fulton J. Sheen once said, “Patience is power. Patience is not an absence of action; rather it is ‘timing’ it waits on the right time to act, for the right principles and in the right way.” And while it might seem really challenging to figure out when the RIGHT time to break up with someone is — “right” is about using good judgment, right is about conforming to certain principles (like integrity and fairness), right is about doing things in order. Now with that in mind, is the RIGHT TIMING now or should it be later?
Only you can really answer that yet what I will say is if your mind, body and spirit aren’t on the same page — figure out why before making any moves. Oh, and if it’s simply about fear — girl, whether it’s November 30, December 9 or January 14…break-ups are always going to be uncomfortable. It’s about knowing what’s best for you and then ending things in a way that is as respectful, timing-wise, as possible (again, due to the whole karma thing).
____
‘Tis the season and sometimes “out with the old” means leaving a relationship behind. Just make sure that you move with wisdom and discernment and not hypersensitivity and knee-jerking.
That way, you can look back on every holiday season with as little regret as possible.
Due to how you handled things. Including a (potential) break-up.
Let’s make things inbox official! Sign up for the xoNecole newsletter for love, wellness, career, and exclusive content delivered straight to your inbox.
Featured image by Shutterstock









